Abstract
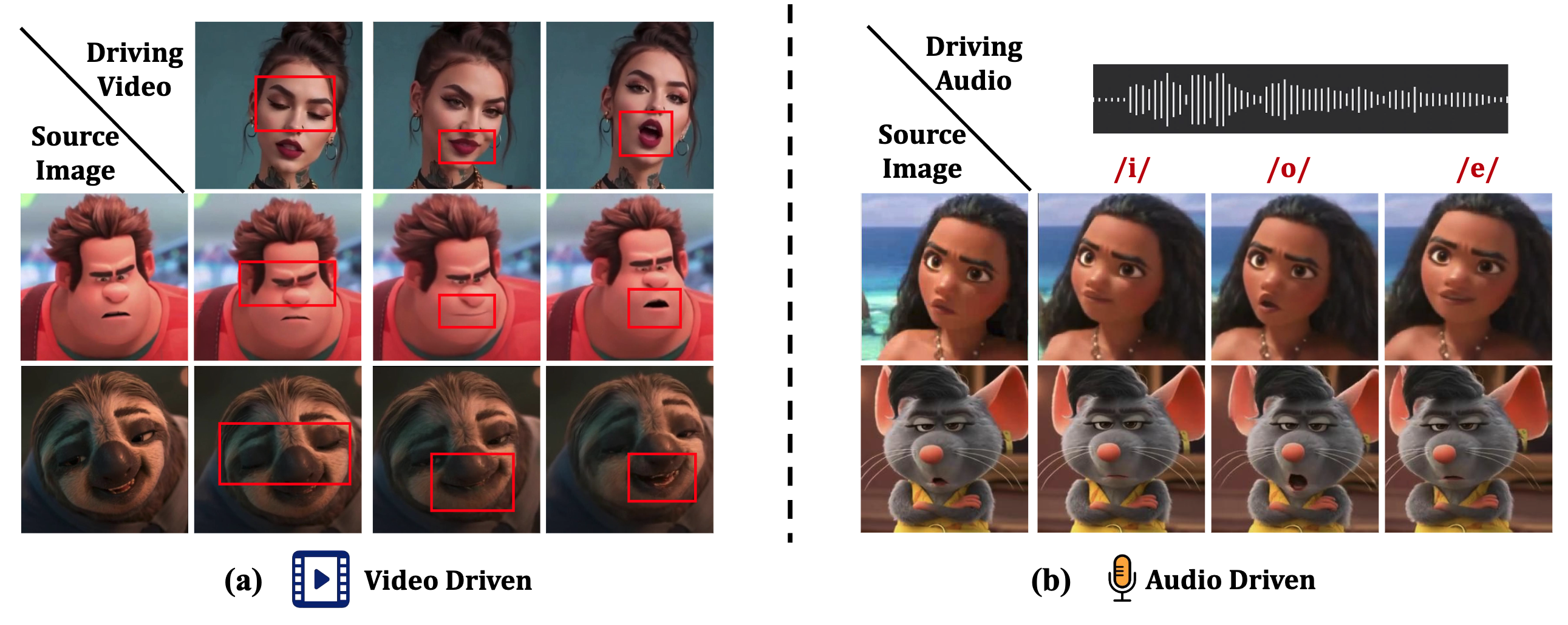
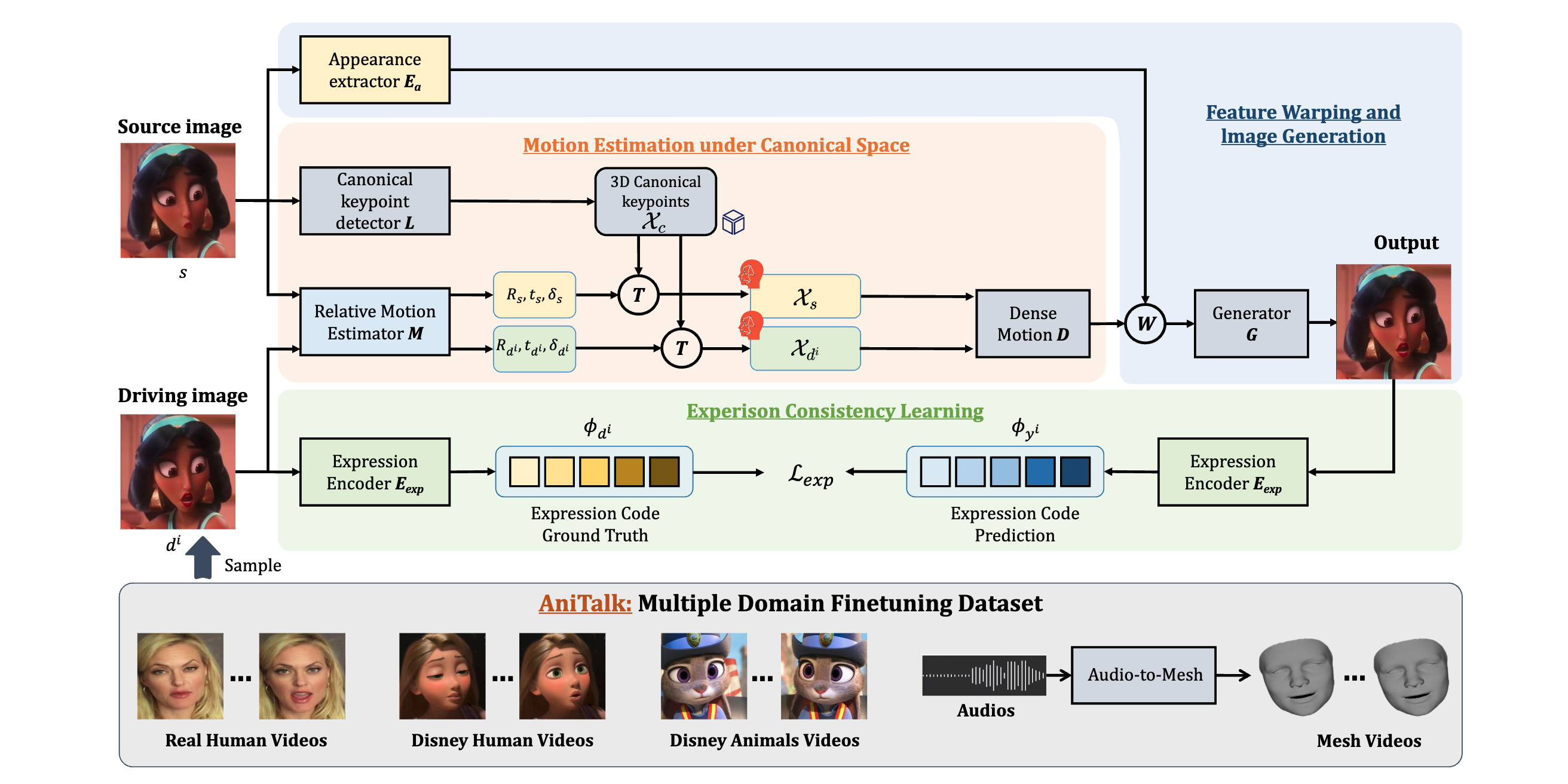
Cross-domain talking head generation has recently garnered increased interest in both research and practical applications due to a rising demand for personalized media, which aims to animate a static image from one domain using a video from another domain. Recent efforts in cross-domain talking head generation typically rely on paired videos or separate frameworks for each domain. Besides, these methods often need extra motion alignment modules across different domains for improved expression reenactment, reducing their versatility. Moreover, previous methods primarily focus on talking heads generation across real human and cartoon human domains, but struggle with cartoon animal animations. To overcome these limitations, we propose AnyTalk, a unified cross-domain talking head generation framework without the need for paired data. Specifically, we first utilize an unsupervised 3D keypoint detector for learning a unified implicit keypoints in canonical space shared by different domains. % enabling precise domain-agnostic motion transfer without additional alignment modules. Then, we devise an expression consistency loss to capture detailed facial dynamics in cross-domain video generation. Furthermore, we introduce a large-scale, high-quality cross-domain talking head dataset called AniTalk, specifically curated to unlock the advanced multi-modal cross-domain generation ability including cross-domain face reenactment and audio-driven facial animation. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority and generalization of AnyTalk for generating high-quality talking head videos driven by multi-modal signals.